Every product team tracks data. Click-through rates, time on task, funnels. These numbers are essential, but they’re not the whole story.
What they lack is some human context: the hesitation before a click, the confusion caused by a label, the frustration hidden behind an abandoned cart. That’s where qualitative testing comes in.
By listening to and observing real users, you uncover the motivations and pain points driving those numbers. When teams combine quantitative scale with qualitative depth, they stop guessing and start building products that truly resonate.
Why Is a Qualitative Testing Platform Needed?

Numbers alone rarely tell the full story. Analytics might show that users are clicking a Sign Up button, but not completing registration. Without asking why, the problem remains a mystery until you hear participants explain that the form feels too long, or that a required field seems irrelevant.
This illustrates what Userlytics describes as the missing why behind the numbers. Metrics can highlight where users drop off, but they cannot explain the confusion, frustration, or hesitation that drives those behaviors. A qualitative testing platform fills this gap by uncovering motivations, emotions, and pain points. Through moderated interviews, remote usability sessions, or real-time feedback, teams gather context that analytics cannot provide. That context fosters empathy, clarifies priorities, and leads to sharper design decisions.
Benefits of Qualitative Testing
Investing in qualitative testing provides advantages that go far beyond what traditional analytics can deliver.
Here are five key benefits:
- Deep Insights into User Motivation
Elicit unfiltered user thoughts, beliefs, and emotions. Instead of just knowing where they click, you’ll understand the why behind their actions, whether it is curiosity, confusion, or frustration.

2. Contextual Understanding
Observe users in real-world environments, remote or in-person, to see how context shapes behavior. A participant juggling tasks on a mobile device may reveal usability barriers invisible in a controlled lab.

3. Narrative-Driven Data
Collect direct quotes, stories, and anecdotes that numbers cannot capture. These narratives humanize findings and inspire empathy across teams.

4. Iterative Discovery
Rapidly test prototypes or new features before large-scale development. As noted in our article on quantitative UX research, pairing early qualitative insights with numbers reduces risk and accelerates iteration.

5. Prioritization & Roadmapping
Use qualitative feedback to rank features by actual user pain points. When participants share frustrations in their own words, prioritization becomes evidence-based rather than assumption-driven.
Ultimately, qualitative testing bridges the gap between what users do and why they do it.

Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Testing
Choosing between qualitative and quantitative testing can feel confusing both provide value, but in different ways. Here s a clear comparison to guide your decision:
| Aspect | Qualitative Testing | Quantitative Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Words, stories, emotions | Numbers, metrics, statistics |
| Methodology | Interviews, open-ended tasks, live observation | Surveys, analytics, A/B tests |
| Depth vs. Breadth | Small sample, deep understanding | Large sample, statistical validity |
| Use Cases | Empathy-building, prototype exploration, uncovering root causes | Benchmarking, performance measurement, statistical validation |
| Cost & Time | Richer insights but more resource-intensive per session | Faster, inexpensive, and scalable |
The two methods don’t compete with each other, rather, they’re complementary. Analytics can show you where users struggle, but qualitative testing reveals why they struggle.
As highlighted in this guide on qualitative vs. quantitative research, the best product teams use both: quantitative for scale, qualitative for empathy. Together, they ensure decisions are grounded in both data and human context.
7 Best Qualitative Testing Tools
From recruiting niche participants to testing early prototypes, every platform on this list adds a piece to the qualitative research puzzle. The next step is figuring out which option best fits your team.
1. Userlytics
Userlytics is a comprehensive qualitative research platform supporting both moderated and unmoderated testing. It helps teams capture real user behaviors, motivations, and emotions.

Features: Video interviews, screen and voice recording, advanced demographic targeting, highlight reels, and the option to combine qualitative and quantitative methods.
Pros:
- Large global panel with advanced filters
- Excellent customer support
- Easy sharing of insights with stakeholders through clips
- Automation features that make processes more efficient
But…
- In order to edit studies once launched, it is necessary to pause the study, edit and then re-launch. In any case, clients can always reach out to their account manager, who will handle any edits.
Pricing: Flexible options, from pay-per-session to enterprise subscriptions.
Explore Userlytics’ qualitative capabilities.
2. Lookback
Lookback offers a collaborative space for live research sessions where teams can observe participants remotely and engage through backchannels during tests.
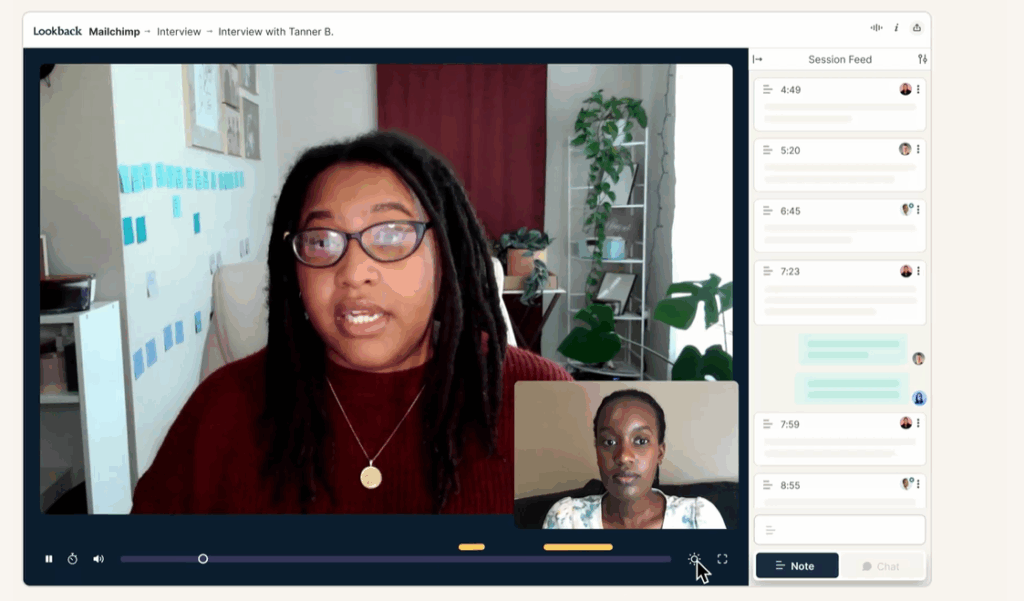
Features: Real-time video observation, screen and face recording, timestamped notes, team chat, and session replays.
Pros:
- Strong live collaboration features for distributed teams
- Integrated note-taking for analysis
But…
- Limited flexibility for unmoderated studies
Pricing: Subscription-based plans, scaling by team size and number of sessions.
3. Dscout
Dscout specializes in diary studies and participant self-recordings, allowing researchers to capture daily experiences and emotions in natural contexts.
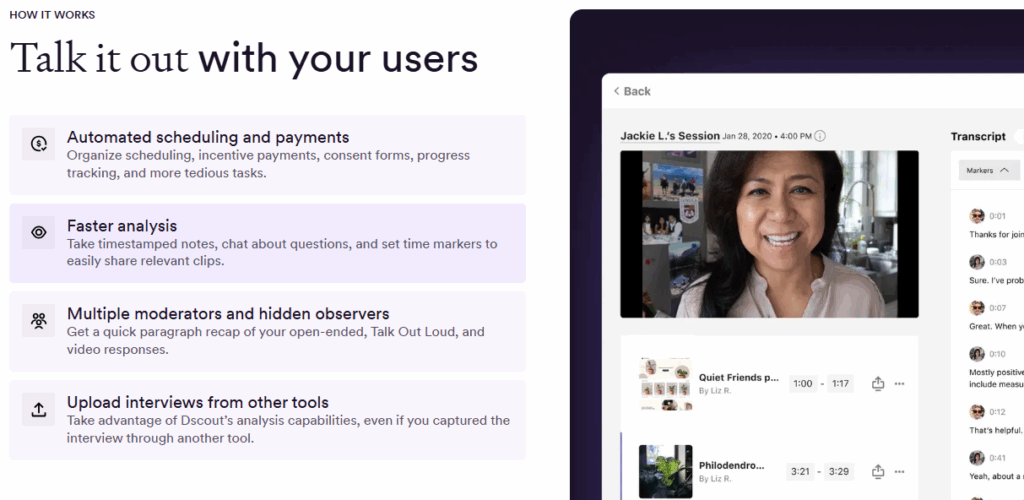
Features:
Video diaries, longitudinal research, survey integration, tagging tools, and participant panel recruitment.
Pros:
- Rich contextual insights from everyday environments
- Longitudinal tracking for deeper discovery
But…
- Reviewing and coding video entries can be time consuming
Pricing: Custom quotes based on project scope and recruitment needs.
4. UserTesting
UserTesting is a well-known platform with a large participant pool and fast turnaround studies. It helps teams gather usability feedback and customer journey narratives quickly.

Features:
Wide participant panel access, video recordings, screen interactions, and sentiment feedback.
Pros:
- Rapid recruitment and quick insights
- Broad audience diversity for consumer testing
But…
- Advanced functionality is often tied to higher pricing tiers
- Reliance on “semi-professional” testers
Pricing: Subscription model with tailored pricing by usage and team size. Can be costly for companies requiring multiple users across the organization.
5. Maze
Maze is designed for prototype testing and early design validation. It integrates with tools like Figma to streamline task flows and collect qualitative context.
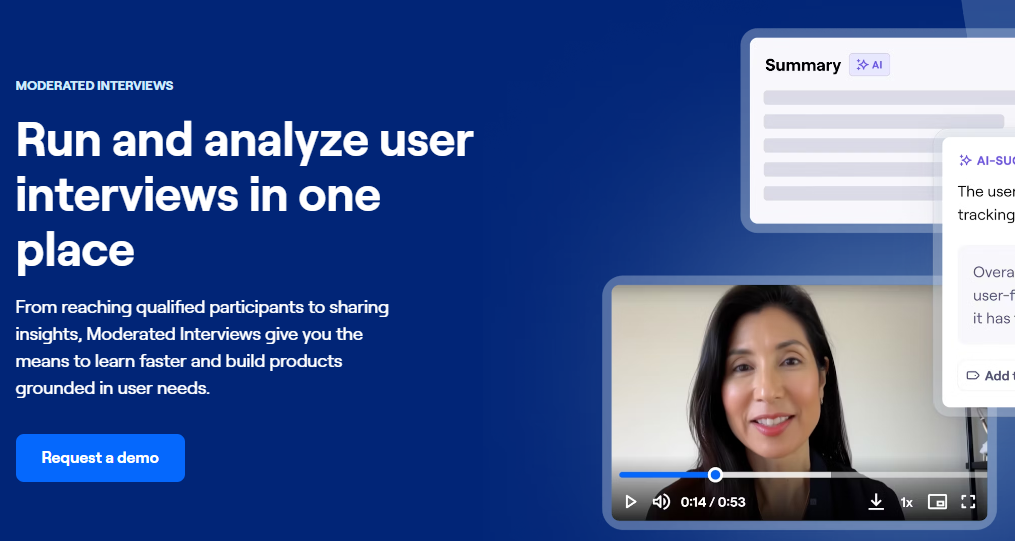
Features:
Prototype testing, usability missions, heatmaps, surveys, and design tool integrations.
Pros:
- Quick setup for prototype validation
- Seamless integration with design workflows
But…
- Users report limited customization options, affecting how they can configure surveys and reports
Pricing: Free plan available, with tiered subscriptions for professional and enterprise use.
6. PlaybookUX
PlaybookUX supports both moderated interviews and unmoderated usability studies. It’s designed for teams that need a flexible research platform with recruitment options.
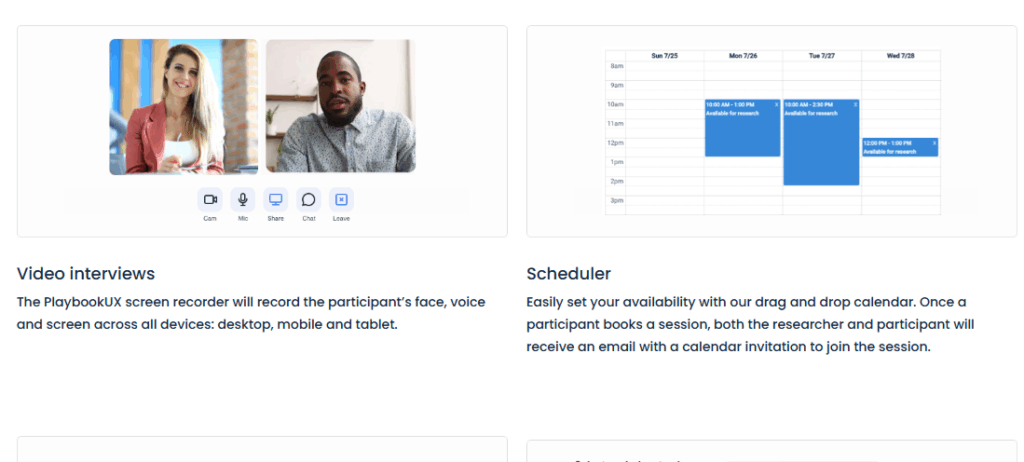
Features:
Video interviews, session recordings, automatic transcriptions, highlight reels, and participant recruitment.
Pros:
- Supports both in-platform recruiting and bring-your-own participants
- Automated transcription and highlights for faster analysis
But…
- The interface may feel complex for new users
Pricing: Subscription-based with monthly or annual billing options.
7. Optimal Workshop
Optimal Workshop is a suite of research tools designed to help teams improve information architecture and usability. It supports a variety of qualitative methods to better understand how users organize and navigate content.

Features:
Surveys and participant recruitment options.
Pros:
- A wide set of tools for usability and information architecture research
- Easy setup for common UX testing methods
But…
- Some users report integration issues
Pricing: Pay-per-respondent model, plus participant incentive costs.
How to Choose the Best Qualitative Testing Tool
Selecting the right platform can feel overwhelming, but a clear framework simplifies the process:
Clarify Your Research Goals
Define if you are validating a brand-new concept, exploring user stories, or diagnosing high-impact usability issues. Goals determine the type of studies you should prioritize.
Assess Participant Needs
Decide if you require a large, diverse participant panel or plan to recruit your own users. Demographic targeting can be critical when researching niche audiences.
Create a Feature Wishlist
List the must-haves: live video interviews, interactive whiteboards, team collaboration tools, automated transcription, or highlight reels for faster analysis.
Evaluate Budget & Pricing Models
Compare pay-per-session, subscription tiers, and à la carte recruiting fees. The right choice depends on frequency, scale, and available budget.
Check Ease of Use & Support
Look for intuitive interfaces and strong onboarding, including training webinars or dedicated customer success managers.
Consider Integration & Sharing
Identify if you need Slack notifications, API hooks, or downloadable clips to share findings with stakeholders quickly.
For example: If your goal is to test an early prototype with healthcare professionals, prioritize platforms that offer prototyping integrations and advanced recruitment filters. This ensures feedback is both context-specific and actionable.
Our Ranking Methodology
To ensure this list is fair and reliable, we applied a consistent evaluation process:
Selection Criteria
- User experience for both moderators and participants
- Depth and quality of qualitative research features
- Participant recruitment flexibility and targeting options
- Pricing transparency and overall value
- Customer support and training resources
Start Qualitative Testing Today
Getting started with qualitative research is easier than you might think. Many platforms, including Userlytics, provide both qualitative and quantitative modules. You can begin with something simple, like a 15-minute remote interview paired with a short post-session survey, to capture valuable insights without a heavy lift.




